Sociology Optional Notes for UPSC CSE
Master the UPSC IAS Sociology Optional syllabus and boost your exam preparation with our in-depth Sociology Optional Notes. Download your free copy today and ace your UPSC IAS journey

Sociology Optional PYQ's (Free)
Download the PDF / Books

Sociology Notes (Click the Link)
Paper 1 and Paper 2

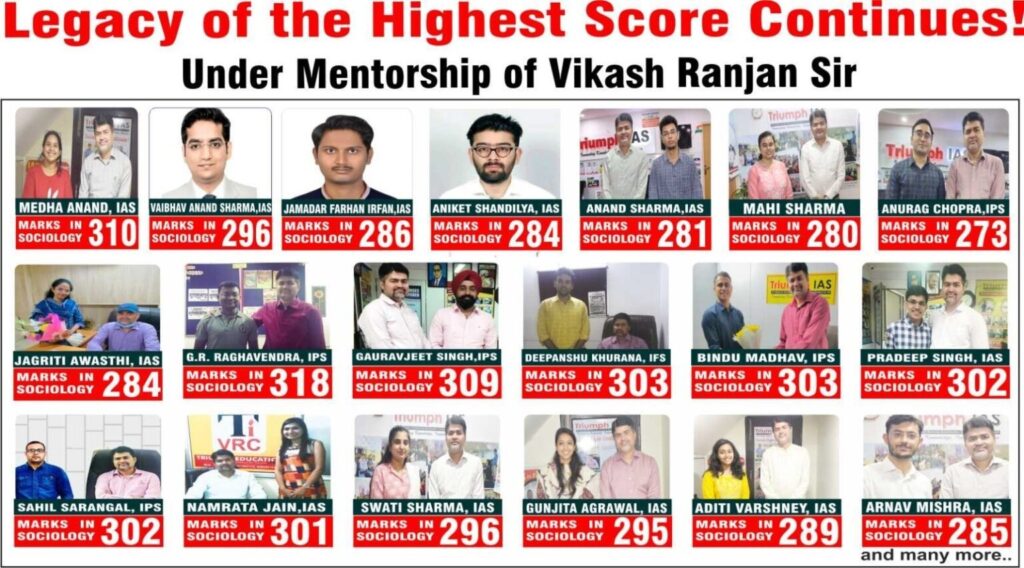
Sociology Toppers (2011-2023)
Sociology optional Toppers

Vikash Ranjan's Sociology Study Material Package + Answer Writing Practice Workbook / Test Papers
Total Number of Booklets - 12 | Nine (9) Booklets Covering 100% Syllabus
One (1) Booklet on PYQ | Two (2) Work Books Consisting 10 Test Papers.
Sociology Optional for UPSC Free Resource Links
Sociology Syllabus
Sociology Optional PYQ'S (Free)
Sociology Optional Books
Sociology Optional Blogs
Basic Concept's of Sociology for Beginners Videos (Free)
How to Approach Sociology? Orientation Class for CSE 2025
Sociology Optional for UPSC @ Triumph IAS
Sociology Foundation Classes (Free Initial Lectures)
Sociology Mentorship Program (Test Series + Mentorship)
Sociology Optional Notes (Buy Now)
Sociology Optional (Free Resources)
Paper - 1 : Sociology Optional Notes (UPSC)
Fundamentals of Sociology
📝Sociology: The Discipline
📖 Modernity and social changes in Europe and emergence of sociology.
📖 Scope of the subject and comparison with other social sciences.
📖 Sociology and common sense.
📝Sociology As Science
📖 Science, scientific method and critique.
📖 Major theoretical strands of research methodology.
📖 Positivism and its critique.
📖 Fact value and objectivity.
📖 Non- positivist methodologies.
📝Research Methods And Analysis:
📖 Qualitative and quantitative methods.
📖 Techniques of data collection.
- Questionnaire
- Interview
- Observation
- Case study
📖 Variables, sampling, hypothesis, reliability and validity.
📝Sociological Thinkers:
📖 Karl Marx - Historical materialism, mode of production, alienation, class struggle.
📖 Emile Durkheim- Division of labour, social fact, suicide, religion and society.
📖 Max Weber- Social action, ideal types, authority, bureaucracy, protestant ethic and the spirit of capitalism..
📖 Talcolt Parsons- Social system, pattern variables.
📖 Robert K. Merton- Latent and manifest functions, conformity and deviance, reference groups.
📖 Mead - Self and identity.
📝Stratification And Mobility:
📖 Concepts- equality, inequality, hierarchy, exclusion, poverty and deprivation.
📖 Theories of social stratification- Structural functionalist theory, Marxist theory, Weberian theory.
📖 Dimensions – Social stratification of class, status groups, gender, ethnicity and race.
📖 Social mobility- open and closed systems, types of mobility, sources and causes of mobility.
📝Works And Economic Life:
📖 Social organization of work in different types of society- slave society, feudal society, industrial /capitalist society.
📖 Formal and informal organization of work.
📖 Labour and society.
📝Politics And Society:
📖 Sociological theories of power.
📖 Power elite, bureaucracy, pressure groups, and political parties.
📖 Nation, state, citizenship, democracy, civil society, ideology.
📖 Protest, agitation, social movements, collective action, revolution.
📝Religion And Society:
📖 Sociological theories of religion.
📖 Types of religious practices: animism, monism, pluralism, sects, cults.
📖 Religion in modern society: religion and science, secularization, religious revivalism, fundamentalism.
📝Systems Of Kinship:
📖 Family, household, marriage.
📖 Types and forms of family.
📖 Lineage and descent.
 Patriarchy and sexual division of labour.
Patriarchy and sexual division of labour.
📖 Contemporary trends.
📝Social Change In Modern Society:
📖 Sociological theories of social change..
📖 Development and dependency.
📖 Agents of social change.
📖 Education and social change.
📖 Science, technology and social change.
Paper - 2 : Sociology Optional Notes (UPSC)
Unit - 1 : Introducing Indian Society
📝Perspectives on the study of Indian society:
📖 Indology (GS. Ghurye).
📖 Structural functionalism (M N Srinivas).
📖 Marxist sociology (A R Desai).
📝Impact of colonial rule on Indian society:
📖 Social background of Indian nationalism.
📖 Modernization of Indian tradition.
📖 Protests and movements during the colonial period.
📖 Social reforms.
Unit - 2 : Social Structure
📝Rural and Agrarian Social Structure:
📖 The idea of Indian village and village studies.
📖 Agrarian social structure - evolution of land tenure system, land reforms.
📝Social Classes in India:
📖 Agrarian class structure.
📖 Industrial class structure.
📖 Middle classes in India.
📝Caste System:
📖 Perspectives on the study of caste systems: GS Ghurye, M N Srinivas, Louis Dumont, Andre Beteille.
📖 Features of caste system.
📖 Untouchability - forms and perspectives.
📝Systems of Kinship in India:
📖 Lineage and descent in India.
📖 Types of kinship systems.
📖 Family and marriage in India.
📖 Household dimensions of the family.
📖 Patriarchy, entitlements and sexual division of labour.
📝Tribal communities in India
📖 Definitional problems.
📖 Geographical spread.
📖 Colonial policies and tribes.
📖 Issues of integration and autonomy.
📝Religion and Society:
📖 Religious communities in India.
📖 Problems of religious minorities.
📖 Patriarchy, entitlements and sexual division of labour.
Unit - 3 : Social Changes In India
📝Visions of Social Change in India
📖 Idea of development planning and mixed economy.
📖 Constitution, law and social change.
📖 Education and social change.
📝Politics and Society
📖 Nation, democracy and citizenship.
📖 Political parties, pressure groups , social and political elite.
📖 Regionalism and decentralization of power.
📖 Secularization.
📝Rural and Agrarian transformation in India
📖 Programmes of rural development, Community Development Programme, cooperatives,poverty alleviation schemes.
📖 Green revolution and social change.
📖 Changing modes of production in Indian agriculture.
📖 Problems of rural labour, bondage, migration.
📝Social Movements in Modern India
📖 Peasants and farmers movements.
📖 Women’s movement.
📖 Backward classes & Dalit movement.
📖 Environmental movements.
📖 Ethnicity and Identity movements.
📝Industrialization and Urbanisation in India
📖 Evolution of modern industry in India.
📖 Growth of urban settlements in India.
📖 Working class: structure, growth, class mobilization.
📖 Informal sector, child labour.
📖 Slums and deprivation in urban areas.
📝Population Dynamics:
📖 Population size, growth, composition and distribution.
📖 Components of population growth: birth, death, migration.
📖 Population policy and family planning.
📖 Emerging issues: ageing, sex ratios, child and infant mortality, reproductive health.
📝Challenges of Social Transformation
📖 Crisis of development: displacement, environmental problems and sustainability.
📖 Poverty, deprivation and inequalities.
📖 Violence against women.
📖 Caste conflicts.
📖 Ethnic conflicts, communalism, religious revivalism.
📖 Illiteracy and disparities in education.

Basic Concept's of Sociology for Beginners Videos (Free)
Enroll now in our Sociology Optional Programme for CSE 2025-26